When and Why does G0 phase occur Biology AnswerBuncom Biology Diagrams Gap 0 Phase (G0) Gap 0 phase or G0 phase of the cell cycle is a period of time where the cell is present in a quiescent stage or resting phase, as it neither divides nor grows. Read More: Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram 6. Cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm into two halves, indicating the

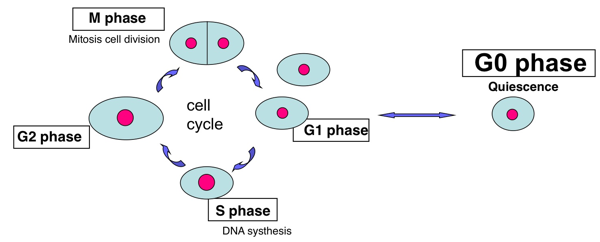
The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase (G0, G1, S, G2) and the mitotic phase (M). The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells undergoing cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA
Cell cycle Biology Diagrams
Learn about the phases of the cell cycle, including interphase and mitosis, in this Khan Academy article.

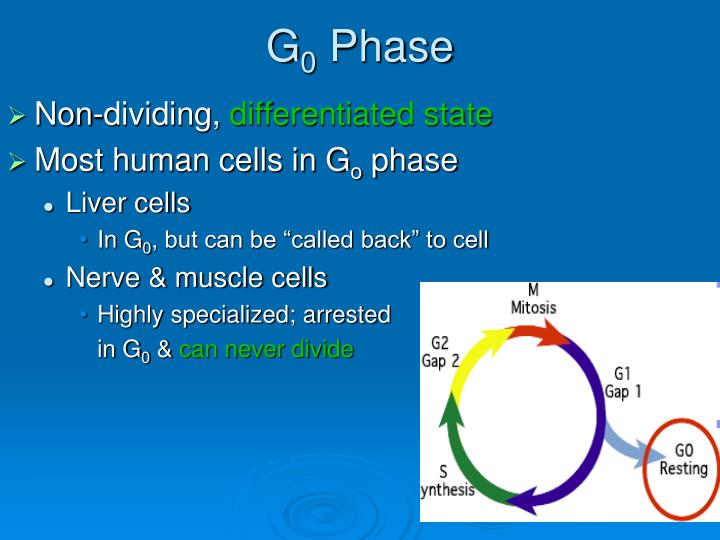
Instead, they exit the G1 growth phase and enter a resting stage called G0-phase. Thus, G0 is also called the alternative phase of the cell cycle. Some cells enter the G0-phase temporarily until an outside signal triggers the onset of G1. In contrast, other cells that either never divide or seldom divide, such as nerve cells or cardiac cells The cell cycle includes the G0 phase, G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase, also known as mitosis. Interphase is the term used to refer to the G1, S, and G2 phases-- although G0 is sometimes The eukaryotic cell cycle consists of four distinct phases: G 1 phase, S phase (synthesis), G 2 phase (collectively known as interphase) and M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). M phase is itself composed of two tightly coupled processes: mitosis, in which the cell's nucleus divides, and cytokinesis, in which the cell's cytoplasm and cell membrane divides forming two daughter cells.

Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
Mitosis in an animal cell (phases ordered counter-clockwise), with G 0 labeled at left. Many mammal cells, such as this 9x H neuron, remain permanently or semipermanently in G 0.. The G 0 phase describes a cellular state outside of the replicative cell cycle.Classically [when?], cells were thought to enter G 0 primarily due to environmental factors, like nutrient deprivation, that limited the