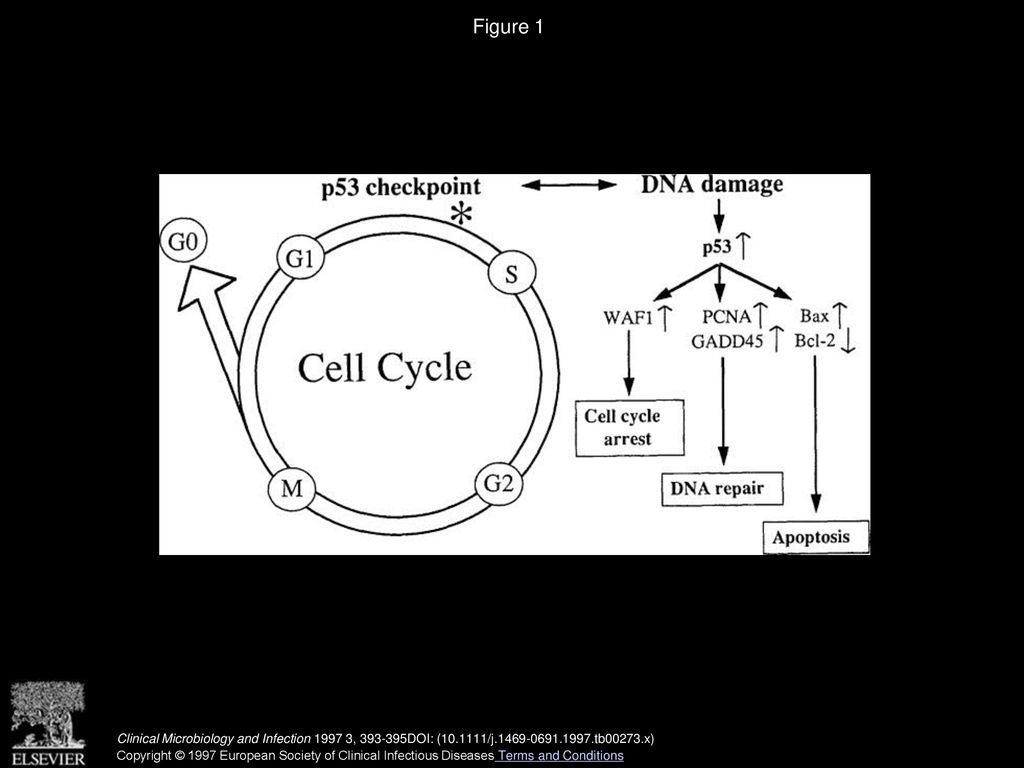
Primary information of p53 gene Biology Diagrams Vastly studied biological processes where p53 has been shown to play a role are cell cycle arrest, senescence, DNA repair, and apoptosis . Over the last few years, researchers have elucidated many other pathways that p53 participates in such as autophagy, cell metabolism, ferroptosis, and pathways that involve the generation of reactive oxygen The tumor suppressor p53 can induce cell cycle arrest. Induction of p53 leads to transcriptional downregulation of many cell cycle genes. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21/WAF1/CIP1/CDKN1A The tumour suppressor p53 has a central role in the response to cellular stress. Activated p53 transcriptionally regulates hundreds of genes that are involved in multiple biological processes
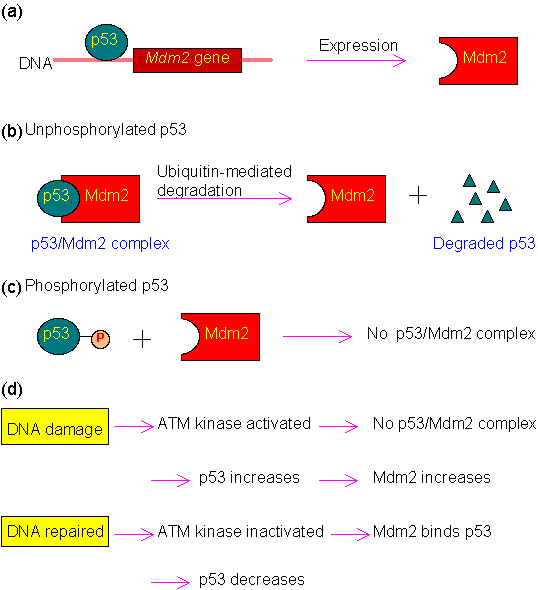
The p53 transcription factor plays a critical role in cellular responses to stress. Its activation in response to DNA damage leads to cell growth arrest, allowing for DNA repair, or directs cellular senescence or apoptosis, thereby maintaining genome integrity. Senescence is a permanent cell-cycle a …
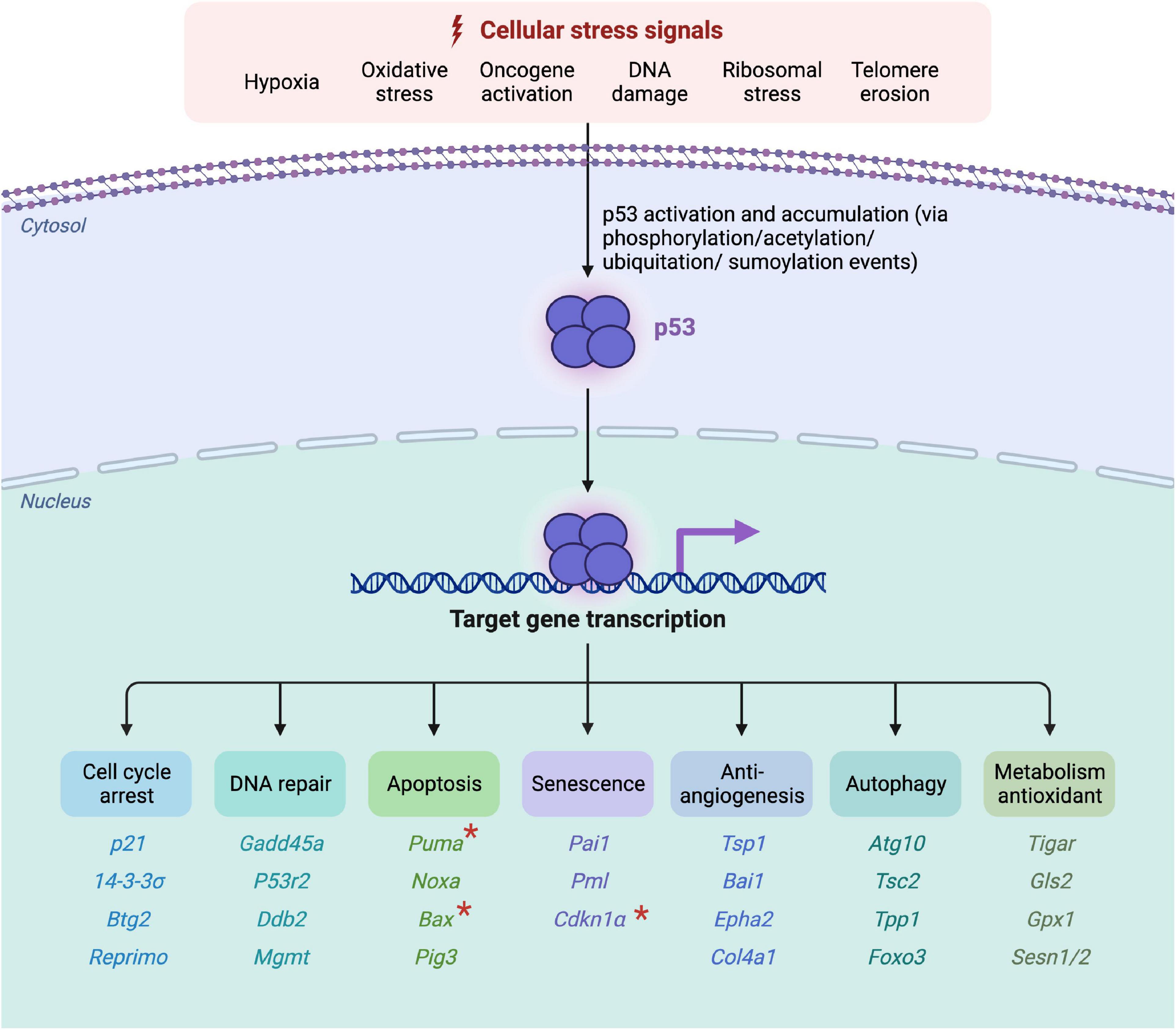
Cell cycle regulation: p53 Biology Diagrams
For example, p53 activation by nutlin-3a results in apoptosis in some cells but cell cycle arrest and senescence in others (both malignant and nontransformed). 67 Moreover, restoration of wild Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis are the most noticeable biological outcomes of p53 activation in cell culture and animal experiments. The seminal finding of p53 as an inhibitor of oncogene-mediated transformation in foci formation is likely the result of its cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis activities (Finlay et al. 1989).The mammalian p53 DNA-binding domain has marginal thermostability, which

P53 is a transcription factor highly inducible by many stress signals such as DNA damage, oncogene activation, and nutrient deprivation. Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis are the most prominent outcomes of p53 activation. Many studies showed that p53 cell-cycle and apoptosis functions are important fo …
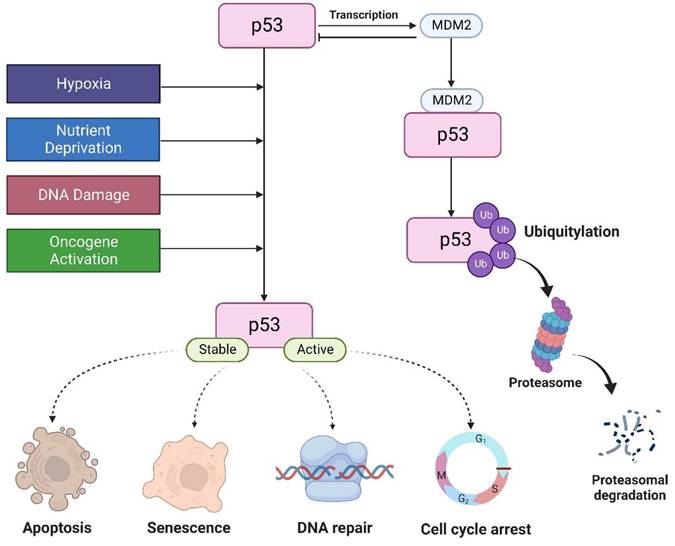
Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor ... Biology Diagrams
The tumor suppressor gene p53, implicated in diverse types of human tumors, functions both as a gene-specific transcription factor as well as a specific inhibitor of the transcription of certain genes: The two physiological outcomes of re-expression of wild type p53 in tumor cells, not expressing wild type p53, are G 1 arrest and apoptosis. The mechanism of G 1 arrest by p53 is much better